Description
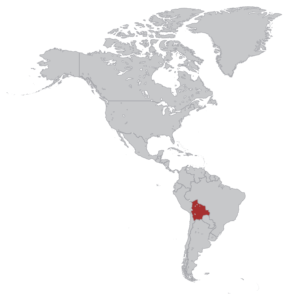 Bolivia, officially the Plurinational State of Bolivia, is a landlocked country located in western-central South America. The capital is Sucre, while the seat of government and financial centre is located in La Paz. The largest city and principal industrial centre is Santa Cruz de la Sierra, located on the Llanos Orientales (tropical lowlands), a mostly flat region in the east of the country. The sovereign state of Bolivia is a constitutionally unitary state, divided into nine departments. Its geography varies from the peaks of the Andes in the West to the Eastern Lowlands, situated within the Amazon Basin. It is bordered to the north and east by Brazil, to the southeast by Paraguay, to the south by Argentina, to the southwest by Chile, and to the northwest by Peru. One-third of the country is within the Andean mountain range. With 1,098,581 km2 (424,164 sq mi) of area, Bolivia is the fifth largest country in South America, after Brazil, Argentina, Peru and Colombia (and alongside Paraguay, one of the only two landlocked countries in the Americas), the 27th largest in the world, the largest landlocked country in the Southern Hemisphere and the world’s seventh largest landlocked country, after Kazakhstan, Mongolia, Chad, Niger, Mali and Ethiopia.
Bolivia, officially the Plurinational State of Bolivia, is a landlocked country located in western-central South America. The capital is Sucre, while the seat of government and financial centre is located in La Paz. The largest city and principal industrial centre is Santa Cruz de la Sierra, located on the Llanos Orientales (tropical lowlands), a mostly flat region in the east of the country. The sovereign state of Bolivia is a constitutionally unitary state, divided into nine departments. Its geography varies from the peaks of the Andes in the West to the Eastern Lowlands, situated within the Amazon Basin. It is bordered to the north and east by Brazil, to the southeast by Paraguay, to the south by Argentina, to the southwest by Chile, and to the northwest by Peru. One-third of the country is within the Andean mountain range. With 1,098,581 km2 (424,164 sq mi) of area, Bolivia is the fifth largest country in South America, after Brazil, Argentina, Peru and Colombia (and alongside Paraguay, one of the only two landlocked countries in the Americas), the 27th largest in the world, the largest landlocked country in the Southern Hemisphere and the world’s seventh largest landlocked country, after Kazakhstan, Mongolia, Chad, Niger, Mali and Ethiopia.
The national flag of Bolivia was originally adopted in 1851. The state flag and ensign (and war flag) is a horizontal tricolour of red, yellow and green with the Bolivian coat of arms in the centre. According to one source, red stands for Bolivia’s brave soldiers, while green symbolises fertility and yellow the nation’s mineral deposits. Along with Haiti, Afghanistan, and Costa Rica, it is one of four national flags in the world which has a depiction of its flag within the flag itself.